Summary
The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, operates independently but remains accountable to Congress and the public. Its principal responsibility is to manage monetary policy, particularly setting the target for the federal funds rate, at meetings of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). The President of the United States appoints the Board of Governors, leading to debates about the Fed’s independence. Recent policy uncertainties, notably surrounding tariffs and trade issues introduced by President Donald Trump’s administration, have complicated the Fed’s task of controlling price growth without pushing the economy into recession. In response, Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell has reiterated the importance of the Fed’s autonomy, stating that decisions should be based on economic data rather than political demands.
Powell’s stance in the face of Trump’s administration policies has been significant in shaping the Federal Reserve’s decisions. Despite concerns over the impact of Trump’s proposed tariffs and other policies, Powell has assured patience in monetary policy given the high level of uncertainty. Although Trump has expressed his preference for lower interest rates, Powell maintains that the Federal Reserve’s primary responsibility is to act in the best interest of all Americans.
The Federal Reserve’s response to Trump’s policies has been a matter of attention. The potential for Trump’s policies, especially on trade, to slow growth to the point that the Federal Reserve would need to decrease interest rates has raised concerns. However, Powell has stated it’s too early to evaluate these effects. This speaks to the Federal Reserve’s crucial role in regulating and supervising the financial system and its mandate to promote maximum employment and stable prices.
The interplay between the Federal Reserve and the presidency becomes more complicated due to the substantial influence that the Fed’s decisions have on the economy and consequently, the political climate. Despite this, the Federal Reserve is expected to evaluate the impact of Presidential policies objectively, as they have significant implications for the economy and politics of the United States. It is also bound by its dual mandate of maintaining price stability and low unemployment. Amid these complex dynamics, the Federal Reserve is poised to continue its focus on its mandate, irrespective of political pressures.
Background
The Federal Reserve, often referred to as “the Fed,” is a central bank in the United States that operates independently of the federal government. This institution is an independent government agency that is held accountable by the public and Congress. To maintain transparency and accountability, the Federal Reserve Chair and other staff members testify before Congress and submit a report on recent economic developments and plans for monetary policy twice a year.
The Fed’s primary task is to make decisions on monetary policy, specifically setting the target for the federal funds rate. This is done at meetings of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which includes the members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining 11 Reserve Bank presidents. The FOMC analyses up-to-date economic data, reviews reports, and surveys from various sectors to determine the appropriate stance for monetary policy.
Despite its independence, the Federal Reserve is subject to influence from the federal government. The President of the United States appoints the Board of Governors, which is then approved by Congress. There has been an ongoing debate regarding the independence of the Federal Reserve, particularly in light of its significant influence over the economy.
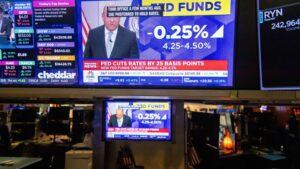
In recent times, the Federal Reserve has faced challenges in navigating monetary policy due to policy uncertainties, notably surrounding tariffs and trade issues introduced by President Donald Trump’s administration. These uncertainties have complicated the task of keeping borrowing costs elevated enough to control price growth without pushing the economy into a recession. During his 2024 election campaign, President Trump insisted on having a say in the Fed’s interest rate policies, intensifying discussions around the influence of political leadership over the Federal Reserve. Despite these challenges, Jerome H. Powell, the Federal Reserve Chair, has maintained a cautious stance, stating that economies function best without tariffs on their trading partners.
Powell’s Statement
Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell has consistently defended the independence of the central bank throughout his career. Powell emphasized during a New York Times event in December that the central bank’s autonomy is intended for the benefit of all Americans, permitting it to base decisions on economic data, not on the wishes of elected officials. In response to President Trump’s demands, Powell assured that neither he nor his colleagues would be influenced, though he refused to engage in a contentious exchange with the president.
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) plays a crucial role in easing or tightening monetary policy, which initiates a sequence of events. The Committee’s decisions must successfully align with its dual mandate objectives. This flexibility allows the Federal Reserve to focus on the long-term, make decisions based on data and objective analysis, and act in the best interest of all Americans. Powell’s statements and actions in the Federal Reserve are particularly significant in the context of Trump’s administration, with its policies on trade and immigration expected to shape the central bank’s decisions. Each year, the FOMC outlines its monetary policy goals and the strategies for achieving them in a public statement. However, the current state of the economy relies on multiple financial measures, which some researchers have consolidated into a simple Financial Conditions Index (FCI).
Markets have expressed concern over Trump’s proposals, including those related to tariffs. In response, Powell reasserted his commitment to patience on monetary policy given the high level of uncertainty. He acknowledged that the White House was introducing significant policy changes in four areas, namely trade, immigration, fiscal policy, and regulation.
It is yet unclear what the extent and timing of Trump’s various policy actions will be. Trump has, however, expressed his preference for lower interest rates. Analysts anticipate the president might criticize Fed Chair Jerome Powell if his actions do not align with Trump’s economic goals. Despite these pressures, Powell maintains that the central bank’s primary responsibility is to act in the best interest of all Americans, and will continue to do so.
Impact of Trump’s Policies on the Federal Reserve
Donald Trump’s ability to influence the Federal Reserve or alter its leadership has gained attention due to his declarations about the need for lower interest rates. There have been concerns that Trump’s economic strategies, particularly on trade, may slow down growth so drastically that the Federal Reserve will have to decrease interest rates to counterbalance the inflation caused by his import taxes and increased costs for businesses and consumers.
Although Trump is advocating for the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates, his own strategies could oppose this by instigating inflation. For instance, his threats of widespread tariffs could lead to higher prices for consumers, while mass deportations could limit the workforce, making it harder to maintain price stability. Nonetheless, Jerome Powell, the chairman of the Federal Reserve, considers it too early to evaluate the effects of these or other policies from Trump’s administration.
Monetary policy, managed by the nation’s central bank (in this case, the Federal Reserve), can significantly influence the shape of the country’s economy. The federal funds rate, which is determined by the Federal Reserve, does not directly impact most businesses and households in the economy. Instead, monetary policy affects the broader economy by influencing general financial conditions, including long-term interest rates for business and household loans, the dollar’s exchange value, and the prices of key assets like equities and real estate.
The challenge lies in determining which aspects of inflationary pressures are caused by policy changes and need to be addressed by monetary policy. These policies’ potential impacts must be considered within the broader context of the Federal Reserve’s mandate to promote maximum employment and stable prices, as well as its role in fostering financial system stability.
Members of the Board of Governors serve fourteen-year terms, with the Chair’s term beginning in the middle of a President’s four-year term. This arrangement aims to insulate the Chair and other members from political pressure. The Federal Reserve sets interest rate policy and plays a role in regulating and supervising the financial system, with its policies intended to meet its dual mandate of price stability and low unemployment. As these decisions significantly impact the economy and consequently, the political climate, politicians may seek to influence the Federal Reserve’s decisions.
Federal Reserve’s Response to Trump’s Policies
During President Donald Trump’s term, the relationship between the administration and the Federal Reserve drew attention. Trump’s ability to influence the Federal Reserve or shake up its leadership were intensifying amid the president’s statements about his desire for lower interest rates. In his 2024 election campaign, Trump insisted that as president he should have a “say” in the Fed’s interest rate policies. However, as an independent central bank, the Federal Reserve has an obligation to be accountable and transparent, performing its duties without undue political pressure or interference from vested interests inherent in electoral politics, fiscal policymaking, and private banking.
Trump’s initial policy proposals raised concern at the Federal Reserve about higher inflation, with firms telling the U.S.. The predominant concern became that Trump’s economic policies, especially on trade, would be such a drag on growth that the Federal Reserve would have to cut interest rates to counteract the inflation that Trump was also baking in with his import taxes and higher prices for businesses and consumers. The Federal Reserve officials, hence, saw a rising risk that inflation might remain sticky in the US.
Federal Reserve Chairman, Jerome Powell, stated that despite elevated levels of uncertainty, the US economy continues to be in a good place. Powell emphasized that they were not in a hurry and were well positioned to wait for greater clarity, despite the Trump administration’s whipsawing on trade policy which has sowed uncertainty for America’s decision makers. Federal Reserve officials also noted that they would be watching the impact of Trump administration policies on inflation as they assess how much further interest rates should fall. Powell mentioned that the path to sustainably returning inflation to the Federal Reserve’s target had been bumpy, and this was expected to continue.
Moreover, as the Federal Reserve conducts monetary policy, it influences employment and inflation primarily through using its policy tools to affect overall financial conditions, including the availability and cost of credit in the economy. These financial conditions, in turn, can be summarized through a financial conditions index (FCI).
The Federal Reserve, maintaining its operational independence as provided by Congress, aimed to navigate the challenges posed by the Trump administration’s policies, keeping its focus on its mandate of maximum employment and stable prices.
Evaluation of the Impact of Presidential Policies by the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve, as the central banking system of the United States, has significant influence over the nation’s financial affairs, impacting the cost of various forms of consumer debt, such as mortgages, credit cards, and automobile loans. Its Board of Governors, excluding the Chair and Vice Chair, are appointed to fourteen-year terms, which start during the middle of a President’s term. This arrangement is designed to insulate the Chair, the Vice Chair, and the members of the board from political pressure.
The Federal Reserve has a dual mandate of maintaining price stability and low unemployment, and its policy decisions are aimed at achieving these goals. As the Federal Reserve’s decisions have a profound impact on the economy, they, in turn, shape the political climate. For this reason, there have been instances where politicians have attempted to influence the Federal Reserve’s decisions. For instance, during his re-election campaign in 1972, Richard Nixon reportedly pressured Fed Chairman Arthur Burns to stimulate the economy.
The Federal Reserve also has a crucial role in regulating and supervising the financial system. Therefore, it is bound to evaluate and respond to the potential impact of Presidential policies on the nation’s economy. The Chair of the Federal Reserve, who is appointed by the President, reports to Congress, underlining the significant interface between the Federal Reserve and the political system.
Federal Reserve’s Dual Mandate
The Federal Reserve Act dictates that the Federal Reserve must conduct monetary policy in order to effectively promote the goals of maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates. While the Act stipulates three distinct objectives for monetary policy, the mandate is typically referred to as the ‘dual mandate’ due to the interconnectedness of these objectives. In an economy where individuals who want to work either have a job or are likely to find one fairly quickly, and where the price level is stable, conditions are set for interest rates to settle at moderate levels. Decisions about monetary policy are made at meetings of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC).
Maximum Employment
Maximum employment, or full employment, is considered to be the highest level of employment that the economy can sustain without causing unwelcome inflation. This denotes an economy where nearly everyone who wants to work has a job. Congress instructs the Federal Reserve to aim for maximum employment, but the definition of this term is not as straightforward as it may appear. In its monetary policy strategy statement, the FOMC has noted that “the maximum level of employment is a broad-based and inclusive goal that is not directly measurable and changes over time owing largely to nonmonetary factors that affect the structure and dynamics of the labor market.
Price Stability
The Fed has defined price stability as an average inflation rate of 2%. Prices are considered stable when consumers and businesses do not have to worry about significant increases or decreases in costs when planning or making long-term borrowing or lending decisions. According to the FOMC, an inflation rate of 2 percent over the longer run, as measured by the annual change in the price index for personal consumption expenditures, aligns best with the Fed’s price stability mandate.
Financial Conditions Impact
As the Federal Reserve implements its monetary policy, it primarily affects employment and inflation by using its policy tools to influence the overall financial conditions, including the availability and cost of credit in the economy. In light of the evolving economic landscape, changes in monetary policy may be necessary, taking into consideration the goals, time horizon, and risk tolerance in the current interest rate environment.
Further Clarity on Trump’s Policies
President Donald Trump’s expressed influence on the Federal Reserve and potential restructuring of its leadership were heightened during his 2024 election campaign. It was during this time he insisted that he should have input in the Federal Reserve’s interest rate policies. His clear preference was for lower interest rates, a view he has expressed on multiple occasions.
Amid nervous markets and President Trump’s proposed tariffs among other uncertainties, Jerome Powell, the chair of the Federal Reserve, advised patience in relation to monetary policy. He stated that the White House was currently in the process of making significant policy changes in areas including trade, immigration, fiscal policy, and regulation.
However, the specifics and timing of these policy actions remained unclear, fueling a sense of uncertainty and apprehension among Federal Reserve officials and markets.
There was an increased concern among Federal Reserve officials that inflation might remain sticky in the US as they started grappling with the potential impacts of incoming policies from Trump’s administration. A change in the Federal Reserve’s strategy was noticeable in August 2020, where a shift was made to respond to “shortfalls of employment from its maximum level” rather than the previous “deviations from its maximum level”. This suggested the Federal Reserve would not tighten monetary policy preemptively only because unemployment was nearing or dropping below estimates of the unemployment rate that economic models indicate are consistent with stable inflation.
Nevertheless, the Federal Reserve remained committed to its mandate to promote maximum employment and stable prices, and to foster the stability of the financial system. As such, the Federal Reserve was prepared to adjust its policy based on new data and objective analysis, and continue to serve the best interests of all Americans. As the Federal Reserve conducts monetary policy, it seeks to affect overall financial conditions, such as the availability and cost of credit in the economy. In March 2020, the FOMC lowered the policy interest rate to near zero, showing the Fed’s flexibility and responsiveness to extraordinary economic conditions.
The content is provided by Jordan Fields, Financial Pulse Now